Lower than two years in the past, the launch of ChatGPT began a generative AI frenzy. Some mentioned the know-how would set off a fourth industrial revolution, fully reshaping the world as we all know it.
In March 2023, Goldman Sachs predicted 300 million jobs can be misplaced or degraded resulting from AI. An enormous shift gave the impression to be underway.
Eighteen months later, generative AI will not be reworking enterprise.
Many tasks utilizing the know-how are being cancelled, reminiscent of an try by McDonald’s to automate drive-through ordering which went viral on TikTok after producing comical failures. Authorities efforts to make methods to summarise public submissions and calculate welfare entitlements have met the identical destiny.
So what occurred?
The AI hype cycle
Like many new applied sciences, generative AI has been following a path referred to as the Gartner hype cycle, first described by American tech analysis agency Gartner.
This extensively used mannequin describes a recurring course of by which the preliminary success of a know-how results in inflated public expectations that finally fail to be realised. After the early “peak of inflated expectations” comes a “trough of disillusionment”, adopted by a “slope of enlightenment” which finally reaches a “plateau of productiveness”.
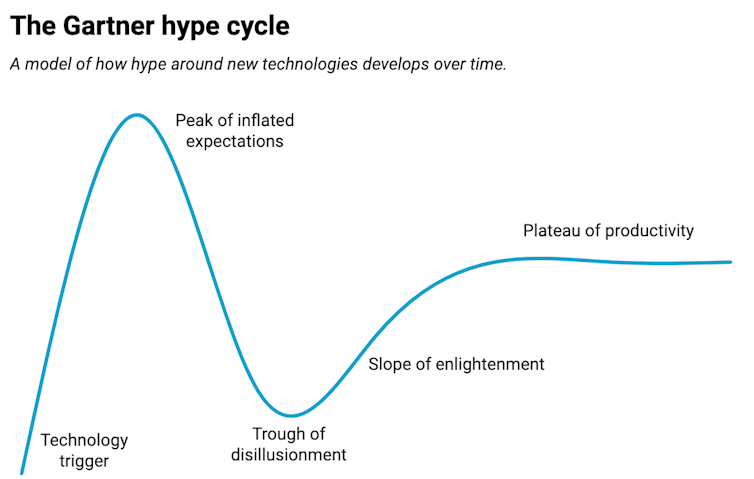
A Gartner report revealed in June listed most generative AI applied sciences as both on the peak of inflated expectations or nonetheless going upward. The report argued most of those applied sciences are two to 5 years away from changing into totally productive.
Many compelling prototypes of generative AI merchandise have been developed, however adopting them in follow has been much less profitable. A examine revealed final week by American assume tank RAND confirmed 80% of AI tasks fail, greater than double the speed for non-AI tasks.
Shortcomings of present generative AI know-how
The RAND report lists many difficulties with generative AI, starting from excessive funding necessities in information and AI infrastructure to a scarcity of wanted human expertise. Nonetheless, the bizarre nature of GenAI’s limitations represents a vital problem.
For instance, generative AI methods can resolve some extremely advanced college admission exams but fail quite simple duties. This makes it very exhausting to evaluate the potential of those applied sciences, which ends up in false confidence.
In spite of everything, if it could resolve advanced differential equations or write an essay, it ought to be capable of take easy drive-through orders, proper?
A current examine confirmed that the skills of enormous language fashions reminiscent of GPT-4 don’t all the time match what folks anticipate of them. Particularly, extra succesful fashions severely underperformed in high-stakes circumstances the place incorrect responses could possibly be catastrophic.
These outcomes counsel these fashions can induce false confidence of their customers. As a result of they fluently reply questions, people can attain overoptimistic conclusions about their capabilities and deploy the fashions in conditions they aren’t fitted to.
Expertise from profitable tasks exhibits it’s powerful to make a generative mannequin comply with directions. For instance, Khan Academy’s Khanmigo tutoring system typically revealed the proper solutions to questions regardless of being instructed to not.
Early on we obtained the mannequin to ask the coed questions nevertheless it wished to reply too. If the coed gave step one, the mannequin then gave the remainder of the steps and the reply. We wrote prompts for the mannequin yelling: DO NOT GIVE THE STUDENT THE ANSWER! 2/6
— Dr. Kristen DiCerbo (@KristenDiCerbo) March 15, 2023
So why isn’t the generative AI hype over but?
There are a couple of causes for this.
First, generative AI know-how, regardless of its challenges, is quickly bettering, with scale and measurement being the first drivers of the development.
Analysis exhibits that the dimensions of language fashions (variety of parameters), in addition to the quantity of knowledge and computing energy used for coaching all contribute to improved mannequin efficiency. In distinction, the structure of the neural community powering the mannequin appears to have minimal affect.
Massive language fashions additionally show so-called emergent skills, that are sudden skills in duties for which they haven’t been educated. Researchers have reported new capabilities “rising” when fashions attain a particular vital “breakthrough” measurement.
Research have discovered sufficiently advanced massive language fashions can develop the flexibility to cause by analogy and even reproduce optical illusions like these skilled by people. The exact causes of those observations are contested, however there isn’t a doubt massive language fashions have gotten extra refined.
So AI firms are nonetheless at work on larger and dearer fashions, and tech firms reminiscent of Microsoft and Apple are betting on returns from their current investments in generative AI. In line with one current estimate, generative AI might want to produce US$600 billion in annual income to justify present investments – and this determine is more likely to develop to US$1 trillion within the coming years.
For the second, the most important winner from the generative AI growth is Nvidia, the most important producer of the chips powering the generative AI arms race.
Because the proverbial shovel-makers in a gold rush, Nvidia not too long ago grew to become probably the most priceless public firm in historical past, tripling its share worth in a single yr to succeed in a valuation of US$3 trillion in June.
What comes subsequent?
Because the AI hype begins to deflate and we transfer by the interval of disillusionment, we’re additionally seeing extra life like AI adoption methods.
First, AI is getting used to assist people, somewhat than substitute them. A current survey of American firms discovered they’re primarily utilizing AI to enhance effectivity (49%), cut back labour prices (47%) and improve the standard of merchandise (58%)
Second, we additionally see a rise in smaller (and cheaper) generative AI fashions, educated on particular information and deployed regionally to scale back prices and optimise effectivity. Even OpenAI, which has led the race for ever-larger fashions, has launched the GPT-4o Mini mannequin to scale back prices and enhance efficiency.
Third, we see a robust give attention to offering AI literacy coaching and educating the workforce on how AI works, its potentials and limitations, and finest practices for moral AI use. We’re more likely to should study (and re-learn) how you can use completely different AI applied sciences for years to come back.
In the long run, the AI revolution will look extra like an evolution. Its use will progressively develop over time and, little by little, alter and remodel human actions. Which is significantly better than changing them.![]()
- Vitomir Kovanovic, Senior Lecturer in Studying Analytics, College of South Australia
This text is republished from The Dialog below a Inventive Commons license. Learn the unique article.